1. Introduction
1.1 Definition of oxygen concentrator
1.2 Importance of oxygen concentrators for individuals with respiratory conditions
1.3 Development of oxygen concentrator
2. How Do Oxygen Concentrators Work?
2.1 Explanation of the process of oxygen concentration
2.2 Types of oxygen concentrators
3. Benefits of Using an Oxygen Concentrator
3.1 Improved quality of life for individuals with respiratory conditions
3.2 Long-term cost savings compared to other oxygen delivery methods
4. Factors to Consider When Choosing an Oxygen Concentrator
4.1 Oxygen concentration stability
4.2 Machine life and failure rate
4.3 Noise level
4.4 Oxygen flow
4.5 Oxygen concentration
4.6 Appearance and portability
4.7 Ease of operation
4.8 After-sales service
4.9 Environmental performance
5. Understanding Oxygen Concentrator Specifications
5.1 Oxygen flow (oxygen output)
5.2 Oxygen concentration
5.3 Power
5.4 Noise level
5.5 Outlet pressure
5.6 Operating environment and conditions
6. How to Use an Oxygen Concentrator Safely and Effectively
6.1 Installation of sanitary environment
6.2 Clean the body shell
6.3 Clean or replace filter
6.4 Clean the humidification bottle
6.5 Clean nasal oxygen cannula
Introduction
1.1 Definition of oxygen concentrator
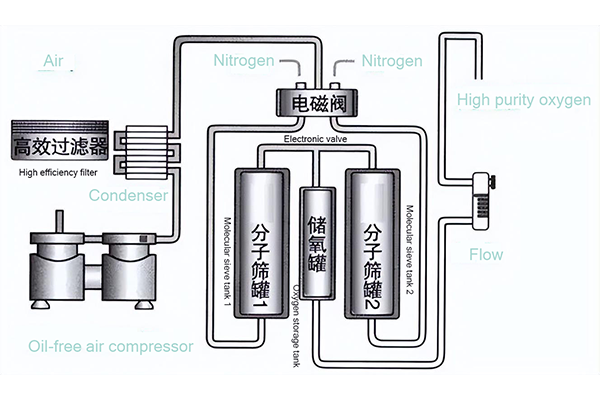
Oxygen generator is a type of machine that produces oxygen. Its principle is to use air separation technology. First, the air is compressed at high density and then the different condensation points of each component in the air are used to separate gas and liquid at a certain temperature, and then distilled to separate it into oxygen and nitrogen. Under normal circumstances, because it is mostly used to produce oxygen, people are accustomed to calling it an oxygen generator.
Oxygen generators usually consist of compressors, molecular sieves, condensers, membrane separators, etc. The air is first compressed to a certain pressure by a compressor, and then separated through a molecular sieve or membrane separator to separate oxygen and other unwanted gases. Next, the separated oxygen is cooled through a condenser, then dried and filtered, and finally high-purity oxygen is obtained.
1.2 Importance of oxygen concentrators for individuals with respiratory conditions
- Provide extra oxygen
Oxygen concentrators can provide additional oxygen to patients to help them fully absorb the oxygen they need
- Reduce breathing difficulties
When a patient uses an oxygen concentrator, it delivers a high concentration of oxygen, increasing the amount of oxygen in the lungs. This can reduce the patient's difficulty breathing and allow them to breathe easier.
- Increase physical vitality
By taking in more oxygen, the energy supply to your body's cells will be boosted. This allows patients to be more energetic in their daily lives, complete more activities, and improve their quality of life.
- Improve sleep quality
Lack of oxygen may prevent them from getting adequate rest, and oxygen concentrators can provide additional oxygen during sleep and improve sleep quality. This allows patients to better recover and improve their energy and concentration during the day.
- Reduce risk of hospitalization
By using oxygen concentrators, patients can get the oxygen they need at home and avoid frequent trips to the hospital. This is not only convenient for patients and their families, but also reduces the pressure on medical resources.
1.3 Development of oxygen concentrator
The first countries in the world to produce oxygen concentrators were Germany and France. The German Linde Company produced the world's first 10 m3/sec oxygen concentrator in 1903. Following Germany, the French Air Liquide Company also began producing oxygen concentrators in 1910. The oxygen concentrator has a history of 100 years since 1903.At that time, it was mainly used in large-scale oxygen production equipment in the industrial field.With the advancement of science and technology and the increase in medical needs, oxygen concentrators have gradually entered the home and medical fields.Modern oxygen production technology is very mature and has been widely used not only in the industrial field, but also in the home and medical fields.
How Do Oxygen Concentrators Work?
2.1 Explanation of the process of oxygen concentration
- Air intake: The oxygen concentrator draws air in through a special air inlet.
- Compression: The inhaled air is first sent to a compressor, so that the gas is compressed to a higher pressure, thereby increasing the density of the gas molecules.
- Cooling: The compressed gas is cooled, which lowers the freezing point of nitrogen and condenses into a liquid at low temperatures, while oxygen remains in a gaseous state.
- Separation: Now the liquid nitrogen can be separated and eliminated, while the remaining oxygen is further purified and collected.
- Storage and distribution: Pure oxygen is stored in a container and can be supplied through pipelines or oxygen cylinders to places where it is needed, such as hospitals, factories, laboratories or other application areas.
2.2 Types of oxygen concentrators
- Based on different purposes of use, they can be divided into medical oxygen concentrators and home oxygen concentrators. Medical oxygen concentrators are mainly used to treat pathological hypoxia, such as respiratory diseases, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, etc., and also have health care functions; home oxygen concentrators are suitable for healthy or sub-healthy people to improve oxygen supply and improve life. quality for purpose
- Based on different purity of product, it can be divided into high-purity oxygen devices, process oxygen devices and oxygen-enriched devices. The purity of oxygen produced by high-purity oxygen devices is above 99.2%; the purity of oxygen produced by process oxygen devices is about 95%; and the purity of oxygen produced by enriched oxygen devices is less than 35%.
- Based on different forms of product, it can be divided into gaseous product devices, liquid product devices and devices that produce gaseous and liquid products at the same time.
- Based on the number of products, it can be divided into small equipment (below 800m³/h), medium equipment (1000~6000m³/h) and large equipment (above 10000m³/h).
- Based on different methods of separation, it can be divided into low-temperature distillation method, molecular sieve adsorption method and membrane permeation method.
- Based on different working pressures, it can be divided into high-pressure devices (working pressure between 10.0 and 20.0MPa), medium-pressure devices (working pressure between 1.0 and 5.0MPa) and full low-pressure devices (working pressure between 0.5 and 0.6MPa).
Benefits of Using an Oxygen Concentrator
3.1 Improved quality of life for individuals with respiratory conditions
Oxygen concentrator lungs are widely used in the treatment of chronic obstructive disease (COPD), pulmonary fibrosis and other diseases. Oxygen concentrators can help patients provide additional oxygen and effectively relieve symptoms such as dyspnea.
3.2 Long-term cost savings compared to other oxygen delivery methods
The cost of oxygen production is low. The system uses air as raw material and only consumes a small amount of electricity when producing oxygen. The system requires very little daily maintenance and has low labor costs.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Oxygen Concentrator
4.1 Oxygen concentration stability
Ensure that the oxygen concentration is stable above 82% to ensure the therapeutic effect
4.2 Machine life and failure rate
Choose an oxygen concentrator with a long life and low failure rate to reduce long-term costs and maintenance needs.
price. Choose the right oxygen concentrator according to your budget, taking into account the balance between price and performance
4.3 Noise level
Choose an oxygen concentrator with less noise, especially for users who need to use the oxygen concentrator for a long time
4.4 Oxygen flow
Choose the appropriate oxygen flow rate according to the user's specific needs (such as health care or treatment)
4.5 Oxygen concentration
Choose an oxygen concentrator that can maintain an oxygen concentration above 90%, which is the standard for medical-grade oxygen concentrators.
4.6 Appearance and portability
Consider the design and size of the oxygen concentrator and choose a model suitable for home use
4.7 Ease of operation
For middle-aged and elderly users or users with limited operating abilities, choose an oxygen concentrator that is simple to operate.
4.8 After-sales service
Choose a brand that provides good after-sales service to ensure safety and convenience of use
4.9 Environmental performance
Consider the environmental performance of the oxygen generator and choose products with less environmental impact
Understanding Oxygen Concentrator Specifications
5.1 Oxygen flow (oxygen output)
Refers to the volume of oxygen output by the oxygen generator per minute. Common flow rates are 1 liter/minute, 2 liters/minute, 3 liters/minute, 5 liters/minute, etc. The larger the flow rate, the suitable uses and groups are also different, such as minor People who are hypoxic (students, pregnant women) are suitable for oxygen concentrators with an oxygen output of about 1 to 2 liters/minute, while people with high blood pressure and the elderly are suitable for oxygen concentrators with an oxygen output of about 3 liters/minute. Patients with systemic diseases and other diseases are suitable for oxygen concentrators with an oxygen output of 5 liters/minute or more
5.2 Oxygen concentration
Refers to the oxygen purity output by the oxygen generator, usually expressed as a percentage, such as concentration ≥90% or 93%±3%, etc. Different concentrations are suitable for different needs and uses.
5.3 Power
Different regions have different voltage standards. For example, China is 220 volts, Japan and the United States are 110 volts, and Europe is 230 volts. When purchasing, you need to consider whether the voltage range of the oxygen concentrator is suitable for the target area of use.
5.4 Noise level
The noise level of the oxygen concentrator during operation, for example ≤45dB
5.5 Outlet pressure
The pressure of oxygen output from the oxygen generator is generally between 40-65kp. The outlet pressure is not always better, it needs to be adjusted according to specific medical needs and patient conditions.
5.6 Operating environment and conditions
Such as temperature, atmospheric pressure, etc., will affect the performance and safety of the oxygen generator.
How to Use an Oxygen Concentrator Safely and Effectively
6.1 Installation of sanitary environment
[Moist environments can easily breed bacteria. Once bacteria enter the respiratory tract, they will affect lung health]
The oxygen generator should be placed in a dry and ventilated environment. The particle screen inside the oxygen generator itself is very dry. If it gets damp, it may cause the nitrogen and oxygen separation process to be blocked, and the machine will not work properly, thus affecting its use.
When not in use, the oxygen generator can be covered with a packaging bag.
6.2 Clean the body shell
[The body of the oxygen concentrator is easily contaminated by the external environment due to long-term exposure to the air]
In order to ensure the hygiene of oxygen use, the machine body should be wiped and cleaned regularly. When wiping, the power supply should be cut off, and then wiped with a clean and soft rag. It is prohibited to use any lubricating oil or grease.
During the cleaning process, be careful not to allow liquid to penetrate into the gaps in the chassis to prevent the power-on body from getting wet and causing a short circuit.
6.3 Clean or replace filter
[Cleaning or replacing the filter can protect the compressor and molecular sieve and extend the life of the oxygen generator]
Clean carefully: To clean the filter, you should first clean it with light detergent, then rinse it with clean water, wait until it is completely dry, and then install it into the machine.
Replace the filter element in time: The filter is generally cleaned or replaced every 100 hours of operation. However, if the filter element becomes black, it should be cleaned or replaced immediately regardless of the length of use.
Warm reminder: Do not operate the oxygen concentrator when the filter is not installed or when it is wet, otherwise it will permanently damage the machine.
6.4 Clean the humidification bottle
[The water in the humidification bottle can humidify and prevent oxygen from being too dry when inhaled into the respiratory tract]
The water in the humidification bottle should be changed every day, and distilled water, purified water or cool boiled water should be injected into the bottle.
The humidification bottle is filled with water. After long use, there will be a layer of dirt. You can drop it into deep vinegar solution and soak it for 15 minutes, then rinse it clean to ensure hygienic use of oxygen.
Recommended cleaning time (5-7 days in summer, 7-10 days in winter)
When the humidification bottle is not in use, the inside of the bottle should be kept dry to prevent bacterial growth.
6.5 Clean nasal oxygen cannula
[The nasal oxygen tube has the most direct contact with the human body, so hygiene issues are particularly important]
The oxygen inhalation tube should be cleaned every 3 days and replaced every 2 months.
The nasal suction head should be cleaned after each use. It can be soaked in vinegar for 5 minutes, then rinsed with clean water, or wiped with medical alcohol.
(Warm reminder: Keep the oxygen tube dry and free of water droplets.)
Post time: Apr-08-2024