A device used to provide oxygen therapy that can continuously provide an oxygen concentration of more than 90% at a flow rate equivalent to 1 to 5 L/min.
It is similar to a home oxygen concentrator (OC), but smaller and more mobile. And because it is small enough/portable, most brands are now certified by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) for use on aircraft.
01 Brief History of Development
Medical oxygen concentrators were developed in the late 1970s.
Early manufacturers included Union Carbide and Bendix Corporation
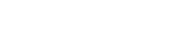
Initially, they were defined as a machine that could replace bulky oxygen tanks and provide a continuous source of home oxygen without frequent transportation.
Jumao has also developed a portable model (POC), which now provides the patient with an oxygen equivalent of 1 to 5 liters per minute (LPM: liters per minute) depending on the patient's respiratory rate.
The latest pulsed products weigh between 1.3 and 4.5 kg, and the continuous (CF) weighs between 4.5 and 9.0 kg.
02 Main functions
Oxygen supply method: As the name implies, it is a method of delivering oxygen to patients
Continuous (continuous)
The traditional oxygen supply method is to turn on the oxygen and continuously output oxygen regardless of whether the patient inhales or exhales.
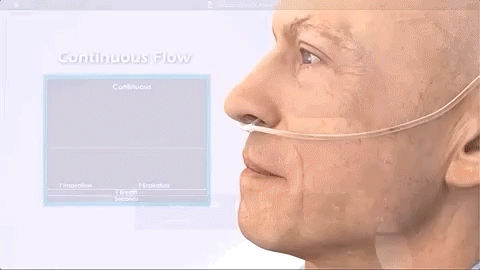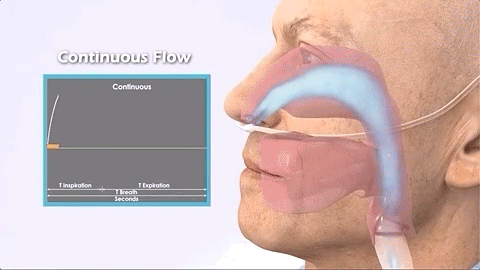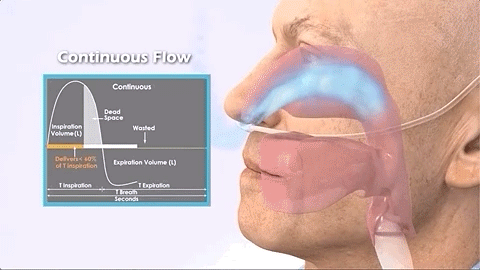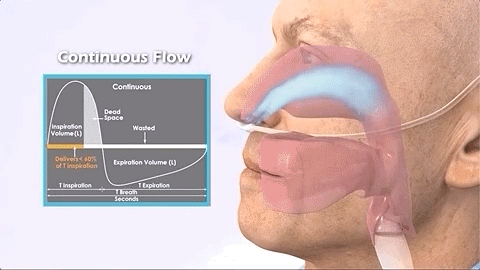
Features of continuous oxygen concentrators:
Providing continuous oxygen concentrators requires larger molecular sieves and compressor components, as well as other electronic equipment. This increases the size and weight of the device by about 9KG. (Note: Its oxygen delivery is in LPM (liters per minute))
Pulse (on-demand)
Portable oxygen concentrators are different in that they only provide oxygen when it detects the patient's inhalation.
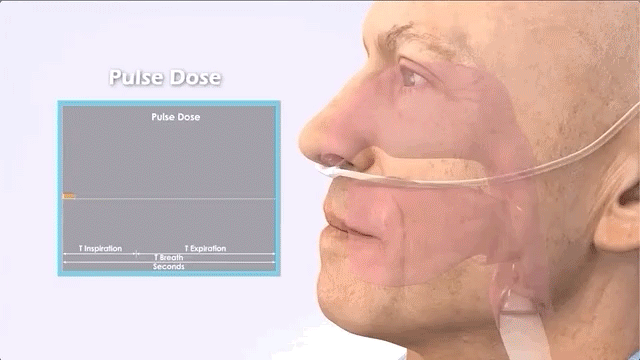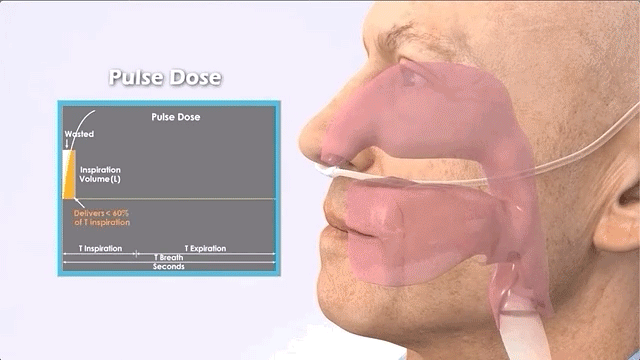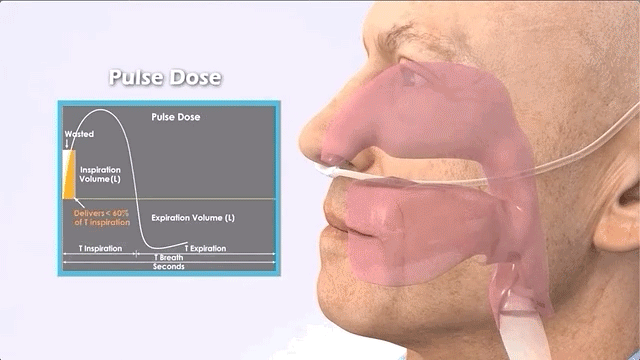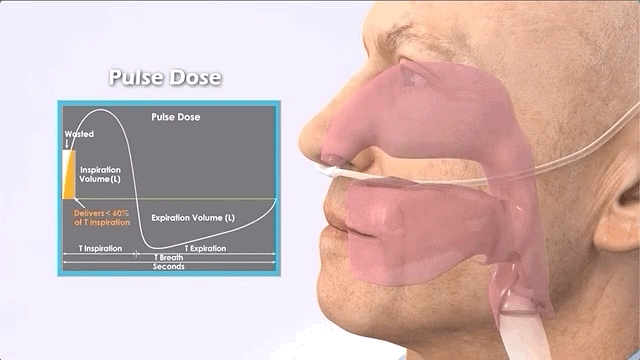
Features of pulse oxygen concentrators:
Pulse (also called intermittent flow or on-demand) POCs are the smallest machines, usually weighing about 2.2 kg.
Because they are small and light, patients will not waste the energy gained from treatment by carrying it.
Their ability to preserve oxygen is key to keeping the device compact without sacrificing oxygen supply time.
Most current POC systems provide oxygen in a pulsed (on-demand) delivery mode and are used with nasal cannula to deliver oxygen to the patient.
Of course, there are also some oxygen concentrators that have both operating modes.
Main components and principles:
The operating principle of POC is the same as that of home oxygen concentrators, both of which use PSA pressure swing adsorption technology.
The main components are small air compressors/molecular sieve tanks/oxygen storage tanks and solenoid valves and pipelines.
Workflow: One cycle, the internal compressor compresses air through the molecular sieve filter system
The filter is composed of silicate particles of zeolite, which can adsorb nitrogen molecules
The atmosphere contains about 21% oxygen and 78% nitrogen; and 1% other gas mixtures
So the filtration process is to separate nitrogen from the air and concentrate oxygen.

When the required purity is reached and the pressure of the first molecular sieve tank reaches about 139Kpa
Oxygen and a small amount of other gases are released into the oxygen storage tank
When the pressure in the first cylinder drops, nitrogen is released
The valve is closed and the gas is discharged into the surrounding air.
Most of the oxygen produced is delivered to the patient, and a portion is sent back to the screen.
To flush out the residue left in the nitrogen and prepare the zeolite for the next cycle.
The POC system is functionally a nitrogen scrubber that can consistently produce up to 90% medical-grade oxygen.
Key performance indicators:
Can it provide sufficient oxygen supplement according to the patient's breathing cycle during its normal operation? To alleviate the harm of hypoxia to the human body.
Can it provide standard oxygen concentration while maintaining the maximum flow gear?
Can it guarantee the oxygen flow required for daily use?
Can it guarantee sufficient battery capacity (or multiple batteries) and charging power cord accessories for home or car use?
03 Uses
Medical Allows patients to use oxygen therapy 24/7,
reducing the mortality rate by about 1.94 times compared to overnight use only.
Helps improve exercise endurance by allowing users to exercise longer.
Helps increase endurance in daily activities.
Compared with carrying an oxygen tank,
POC is a safer choice because it can provide purer gas on demand.
POC devices are always smaller and lighter than canister systems and can provide a longer supply of oxygen.
Commercial
Glassblowing industry
Skin care

04 Aircraft use
FAA approval
On May 13, 2009, the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) ruled
that air carriers operating passenger flights with more than 19 seats must allow passengers who need them to use FAA-approved POCs.
The DOT rule has been adopted by many international airlines

05 Nighttime use
Patients with oxygen desaturation due to sleep apnea are not recommended to use this product, and CPAP machines are usually recommended.
For patients with desaturation due to shallow breathing, nighttime use of POCs is a useful therapy.
Especially with the advent of alarms and technology that can detect when a patient is breathing slower during sleep and adjust the flow or bolus volume accordingly.
Post time: Jul-24-2024